Navitas reference design helps drives AI revolution

GaN integrated power ICs deliver speed, efficiency and small size for power-hungry AI and edge computing.
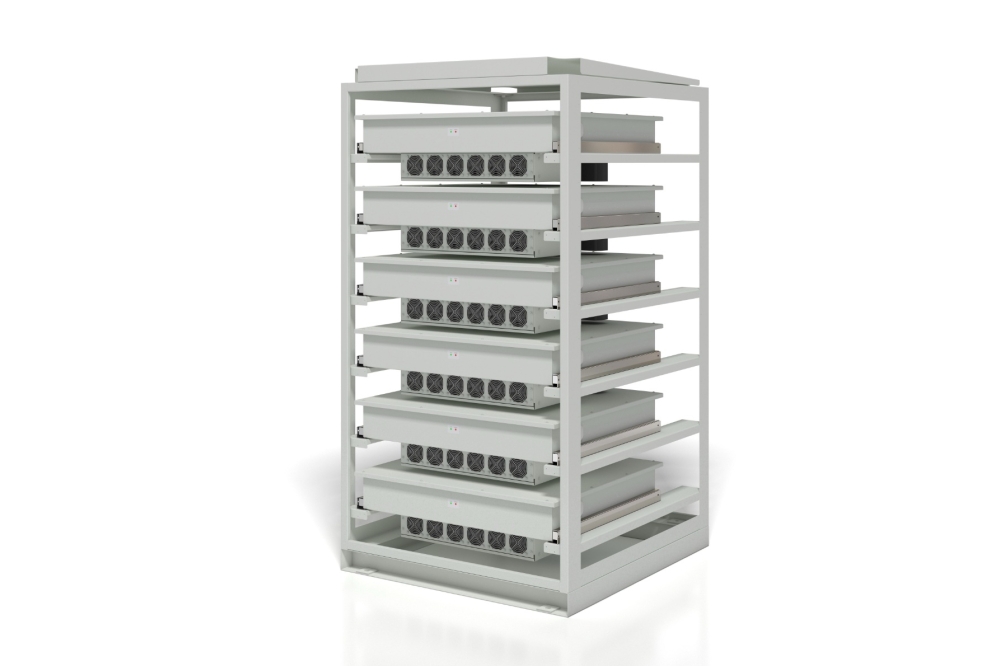
Navitas Semiconductor has announced that its CRPS185 3,200W 'Titanium Plus' server reference design not only surpasses the stringent 80Plus Titanium efficiency requirements, but also satisfies the increasing power demands of AI data centres.
The deployment of AI including OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Microsoft’s Bing with AI, and Google’s Bard, has penetrated all aspects of people's lives. New power-hungry AI processors like NVIDIA’s DGX GH200 ‘Grace Hopper’ demand up to 1,600W each, driving power-per-rack specifications from 30-40 kW up to 100 kW per cabinet. Meanwhile, energy conservation and emission reduction needs, as well as the latest European regulations, mean server power supplies must exceed the 80Plus ‘Titanium’ efficiency specification.
Navitas says its reference designs accelerate customer developments, minimise time-to-market, and set new industry benchmarks in energy efficiency, power density and system cost, enabled by GaNFast power ICs. These platforms include fully-tested hardware, embedded software, schematics, bill-of-materials, layout, simulation and hardware test results.
Navitas’ CRPS185 platform delivers a full 3,200W of power in 1U (40 mm) x 73.5mm x 185 mm (544 cc), achieving 5.9W/cc, or almost 100W/in3 power density. This is a 40 percent size reduction vs, the equivalent legacy silicon approach and exceeds the Titanium efficiency standard, reaching over 96.5 percent at 30 percent load, and over 96 percent stretching from 20 percent to 60 percent load, creating a ‘Titanium Plus’ benchmark, critical for data centre operating models.
The CRPS185 uses an interleaved CCM totem-pole PFC design with full-bridge LLC. The critical components are Navitas’ new 650V GaNFast power ICs, with high-speed integrated GaN drive. Additionally, GaNFast power ICs offer low switching losses, with a transient-voltage capability up to 800V, and other high-speed advantages such as low gate charge (Qg), output capacitance (COSS) and no reverse-recovery loss (Qrr).
As high-speed switching reduces the size, weight and cost of passive components in a power supply, Navitas estimates that GaNFast power ICs save 5 percent of the LLC-stage system material cost, plus $64 per power supply in electricity over 3 years.
Compared to traditional ‘Titanium’ solutions, Navitas say its design, running at a typical 30 percent load, can reduce electricity consumption by 757 kWh, and decrease carbon dioxide emissions by 755 kg over three years. This reduction is equivalent to saving 303 kg of coal. Not only does it help data centre clients achieve cost savings and efficiency improvements, but it also contributes to the environmental goals of energy conservation and emission reduction.
In addition to data centre servers, this solution can also be used in applications such as switch/router power supplies, communications, and other computing applications, according to the company..
“The popularity of AI applications like ChatGPT is just the beginning. As data centre rack power increases by 2x-3x, up to 100 kW, delivering more power in a smaller space is key,” said Charles Zha, VP and GM of Navitas China. “We invite power designers and system architects to partner with Navitas and discover how a complete roadmap of high efficiency, high power density designs can cost-effectively, and sustainably accelerate their AI server upgrades.”